B+树实现细节
目录结构
./src
├── index
│ ├── b_plus_tree.rs
│ └── mod.rs
├── iterator
│ ├── b_plus_tree_iterator.rs
│ └── mod.rs
├── main.rs
└── page
├── b_plus_tree_page.rs
└── mod.rs
m阶B+树的定义
B+树是B树的一种变形形式,m阶B+树满足以下条件:
- 每个节点最多有
m个孩子,至多有m-1个关键字。- 意味着对于内部节点,最多只有
m-1个关键字,最多可以有m个孩子(也就是m个子节点指针)。 - 意味着对于叶子节点,最多可以有
m-1个关键字和孩子(也就是m-1个子节点指针,对于叶子节点来说,关键字和孩子节点指针是一一对应的)。
- 意味着对于内部节点,最多只有
- 除根节点和叶子节点外,每个节点至少有
(m + 1) / 2个孩子,也就是说至少有(m - 1) / 2个关键字。 - 如果根节点不为空,根节点至少有
2个孩子。 - 所有叶子节点增加一个链表指针串联起所有的叶子节点,所有关键字都在叶子节点出现。
举例,当m=3的时候,m阶B+树满足以下条件:
- 内部节点最多只有
2个关键字,最多可以有3个节点指针。 - 叶子节点最多可以有
2个关键字,最多可以有2个节点指针,因为叶子节点的关键字和节点指针是一一对应的。 - 如果根节点不为空,根节点至少有
2个孩子。 - 所有叶子节点增加一个链表指针串联起所有的叶子节点,所有关键字都在叶子节点出现。
B+树节点布局
B+树的节点分为两种,一种是内部节点(internal page),另一种是叶子节点(leaf page)。
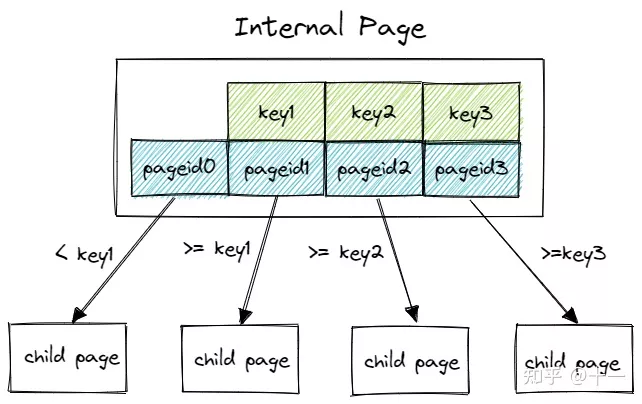
内部节点
如图所示,下图为B+树内部节点的布局,可以很容易看出,key相对于value来说少一个。也就是说,在内部节点中,关键字相对于子节点指针来说少一个,而在程序中,我们一般用Vector来表示这种关系,Vector中每个item为一个kv键值对,key代表提供索引的关键字,而value代表指向子节点的指针。由于关键字相对于子节点来说少一个,因此下标为0位置的key一般不用管它,也就是第0个位置的key不提供关键字检索功能。
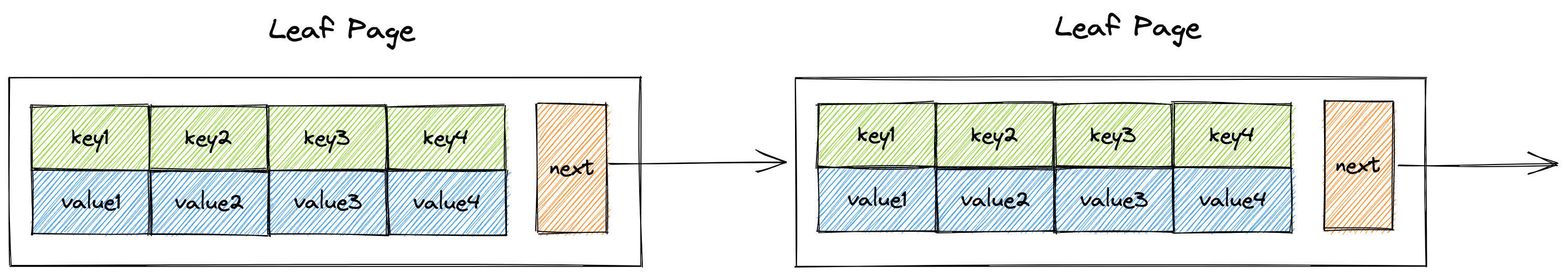
叶子节点
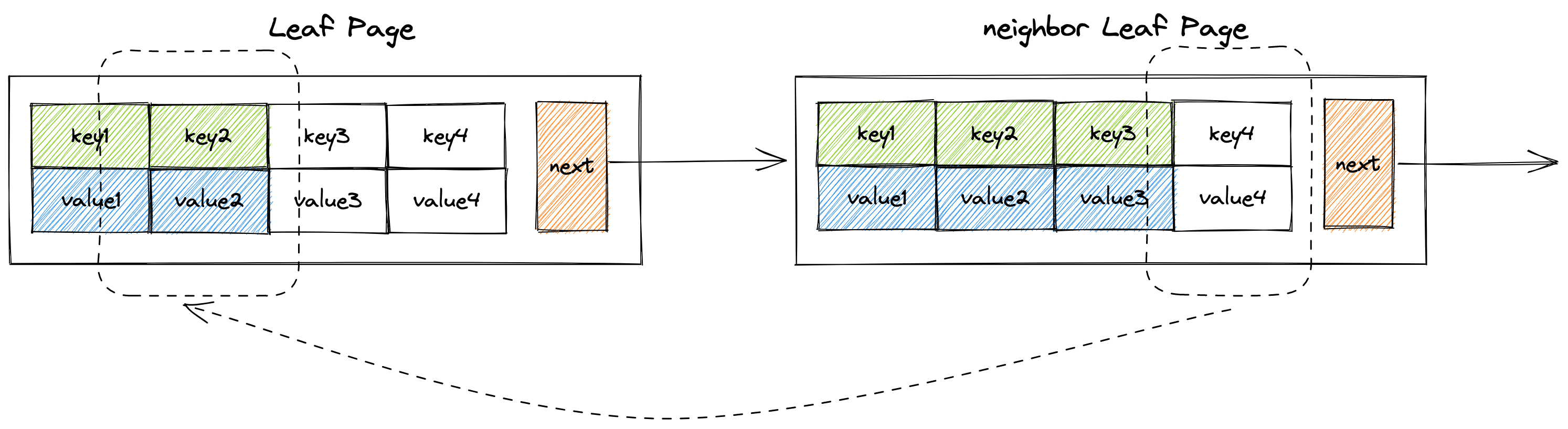
如图所示,下图为B+树叶子节点的布局,可以很容易看出,叶子节点的key与value是一一对应的。同时还存在一个指向下一个叶子节点的next指针,将所有的叶子节点串联成为一个链表。通过将叶子节点串联成一个链表,B+树就可以很方便的实现区间范围检索功能。
B+树节点的代码实现
B+树的节点分为两种,一种是内部节点(internal page),另一种是叶子节点(leaf page)。这里利用rust中的枚举来体现这两类节点类型。
#[derive(PartialEq)]
pub enum BPlusTreePageType {
InvalidIndexPage,
InternalPage,
LeafPage
}
内部节点和叶子节点的公共类
由于Rust语言不太好实现OOP中的继承,因为我在代码中采用了聚合(组合)的方式,将内部节点和叶子节点组合成为一个公共类BPlusTreePage。 这边利用type关键字定义了3个重命名变量,这边简单解释一下:
Page代表子节点指针,由于子节点指针可能为空,因此最外层用Option包裹。由于子节点可能需要在代码中共享传递,因此需要再利用Rc智能指针包一层,由于父节点需要通过子节点指针来修改子节点中的值,所以需要为子节点指针提供内部可变性,因此最里面用RefCell包一层。RcPage代表不为空的子节点指针。在代码编写过程中,很多操作传递的子节点指针一点不为空,而这里的Option显然多余了,于是我们又抽象出一个RcPage代表绝对不为空的子节点指针。
pub type Page = Option<Rc<RefCell<BPlusTreePage>>>;
pub type RcPage = Rc<RefCell<BPlusTreePage>>;
pub type SizeT = usize;
pub struct BPlusTreePage {
page_id_: usize,
page_type_: BPlusTreePageType,
max_size_: SizeT,
page_data_: Vec<MappingType>,
parent_page_: Page,
next_page_: Page
}
| 属性 | 类型 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| page_id_ | usize | 节点ID |
| page_type_ | BPlusTreePageType | 节点类型(内部节点/叶子节点) |
| max_size_ | SizeT | 该节点的最大容量 |
| page_data_ | Vec | 该节点存储的数据 |
| parent_page_ | Page | 该节点的父节点 |
| next_page_ | Page | 如果该节点为叶子节点,则代表该叶子节点的下一个叶子节点 |
节点存储KV数据的MappingType类型
如上所述,我们采用Vector来存储B+树的节点中的简直对结构。其中Vector中的类型即为下面的MappingType类型,它包含一个key和value。追求方便,这边我就简单将键和值的类型都定为i32,后续可以利用范型来实现B+树类型的定制。
#[derive(Clone, Default, PartialEq)]
pub struct MappingType {
pub key: i32,
pub value: ValueType,
}
考虑到内部节点和叶子节点的value类型并不一样,内部节点的value类型为子节点指针,而叶子节点的value类型为B+树所存储的值。于是我利用名为ValueType的枚举类型来表示这两种value类型,如下所示。
#[derive(Clone)]
pub enum ValueType {
Page(Page), // 指代page
Value(Option<i32>) // 指代真正的value
}
节点页面部分方法说明
get_min_size方法
首先get_min_size是一个非常重要的方法,也是一个及其容易出错的方法。顾名思义,该方法显然是获取当前节点页面能存储最少键值对的数量。根据上文所述的B+树定义,分为以下几种情况:
- 如果当前页面为根节点:
- 如果当前根节点为内部节点,对于内部节点来说最少要有
2个键值对(最少可以只有一个关键字,因为下标为0的关键字一般弃用)。 - 如果当前根节点为叶子节点,对于叶子节点来说最少要有
1个键值对。
- 如果当前根节点为内部节点,对于内部节点来说最少要有
- 如果当前页面不为根节点:
- 如果当前页面为内部节点,那么最少要有
(m + 1) / 2个键值对(当m为3时,内部节点最少要有2个键值对,也就是最少要有两个指向子节点的指针,最少只有1个关键字)。 - 如果当前页面为叶子节点,那么最少要有
(m - 1) / 2个键值对(当m为3时,叶子节点最少要有1个键值对)。
- 如果当前页面为内部节点,那么最少要有
pub fn get_min_size(&self) -> SizeT {
return if self.is_root_page() {
if self.is_internal_page() {
2
} else if self.is_leaf_page() {
1
} else {
0
}
} else {
if self.is_internal_page() {
(self.max_size_ + 1) / 2
} else if self.is_leaf_page() {
self.max_size_ / 2
} else {
0
}
}
}
lookup方法
lookup方法一般用于在节点页面中,通过传入一个key,找到该key对应的value。由于B+树节点的key天然具有排序的属性,因此可以采用二分法来加速键值对的查找。可以自己手写upper bound算法,或者调用Vector提供的binary_search方法(使用这种方式需要实现PartialEq和EqTrait)。
pub fn lookup(&self, key: i32) -> ValueType {
if self.is_internal_page() {
let mut left = 1;
let mut right = self.get_size() - 1;
while left <= right {
let mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if self.key_at(mid) > key {
right = mid - 1;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
let target_index = left;
assert!(target_index - 1 >= 0);
self.value_at(target_index - 1)
} else if self.is_leaf_page() {
let target_index = self.key_index(key);
if target_index == self.get_size() || self.key_at(target_index) != key {
ValueType::Value(None)
} else {
self.page_data_[target_index].value.clone()
}
} else {
ValueType::Value(None)
}
}
move_half_to方法
在B+树中有这么一种情况,某个页面插入一个键值对后它的size超过来max_size,此时需要new一个新的页面来分担部分键值对,因此需要调用move_half_to方法来将当前页面一般的键值对转移到新的页面中去。
注意:转移的value如果是子节点指针的话,不要忘记修改子节点的
parent_page属性了,因为键值对转移后,子节点的父节点就变成了新new出来的页面了。
pub fn move_half_to(&mut self, recipient: RcPage) {
let start_index = self.get_min_size();
let pre_size = self.get_size();
let move_num = pre_size - start_index;
let mut moved_items = self.page_data_.split_off(start_index);
for item in &mut moved_items {
match &mut item.value {
ValueType::Page(child_page) => {
(*child_page).as_ref().unwrap().borrow_mut().parent_page_ = Some(recipient.clone());
}
ValueType::Value(_) => {
// todo nothing!
}
}
}
recipient.borrow_mut().page_data_.append(&mut moved_items);
assert_eq!(pre_size - move_num, self.get_size());
}
move_all_to方法
在B+树中还有一种情况,如果某个页面因为删掉一个键值对后,其size小于min size,同时与它相邻的节点页面也没有足够的键值对能够分配,也就是说,当前页面的size + 相邻页面的size <= max_size�,此时这个页面也就没有存在的必要了。因为该页面需要调用move_all_to方法将当前页面剩余的键值对全部移动到它相邻的节点页面中去。
注意:转移的value如果是子节点指针的话,不要忘记修改子节点的
parent_page属性了,因为键值对转移后,子节点的父节点就变成了新new出来的页面了。
pub fn move_all_to(&mut self, recipient: RcPage, middle_key: i32) {
if self.is_internal_page() {
self.set_key_at(0, middle_key);
}
let mut moved_items = self.page_data_.to_vec();
self.page_data_.clear();
for item in &mut moved_items {
match &mut item.value {
ValueType::Page(child_page) => {
(*child_page).as_ref().unwrap().borrow_mut().parent_page_ = Some(recipient.clone());
}
ValueType::Value(_) => {
// todo nothing!
}
}
}
recipient.borrow_mut().page_data_.append(&mut moved_items);
}
move_first_to_end_of方法和move_last_to_front_of方法
在B+树中还有一种情况,如果某个页面因为删掉一个键值对后,其size小于min size,但与它相邻的页面有足够的键值对能借给当前页面。也就是说,当前页面的size + 相邻页面的size > max_size�,这个时候就可以调用move_first_to_end_of方法或者move_last_to_front_of方法,来实现键值对在两个页面之间的重分配。
注意:转移的value如果是子节点指针的话,不要忘记修改子节点的
parent_page属性了,因为键值对转移后,子节点的父节点就变成了新new出来的页面了。
pub fn move_first_to_end_of(&mut self, recipient: RcPage, middle_key: i32) {
if self.is_internal_page() {
self.set_key_at(0, middle_key);
}
assert!(self.page_data_.len() > 0);
let mut first_item = self.page_data_.remove(0);
if self.is_internal_page() {
match &mut first_item.value {
ValueType::Page(child_page) => {
(*child_page).as_ref().unwrap().borrow_mut().parent_page_ = Some(recipient.clone());
}
ValueType::Value(_) => {
// todo nothing!
}
}
}
recipient.borrow_mut().page_data_.push(first_item);
}
pub fn move_last_to_front_of(&mut self, recipient: RcPage, middle_key: i32) {
recipient.borrow_mut().set_key_at(0, middle_key);
assert!(self.page_data_.len() > 0);
let mut last_item = self.page_data_.pop().unwrap();
if self.is_internal_page() {
match &mut last_item.value {
ValueType::Page(child_page) => {
(*child_page).as_ref().unwrap().borrow_mut().parent_page_ = Some(recipient.clone());
}
ValueType::Value(_) => {
// todo nothing!
}
}
}
recipient.borrow_mut().page_data_.insert(0, last_item);
}
B+树的实现
通过上述代码实现B+树的节点页面后,我们就可以开始构建B+树了。对于一般的B+树来说,不可或缺的元素包括internal_max_size_、leaf_max_size_、root_page_等。也就是说,一个B+树一定要有内部节点最大容量和叶子节点最大容量,二者可以相同也可以不同,但一般来说是相同的。同时还需要存储B+树的根节点,B+树的查找、插入和删除操作都是从根节点开始的。
pub struct BPlusTree {
index_name_: String,
internal_max_size_: SizeT,
leaf_max_size_: SizeT,
root_page_: Page
}
| 属性 | 类型 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| index_name_ | String | B+树名称 |
| internal_max_size_ | SizeT | B+树内部节点容量 |
| leaf_max_size_ | SizeT | B+树叶子节点容量 |
| root_page_ | Page | B+树的根节点 |
B+树部分方法说明
find_leaf_page方法
顾名思义,该方法的作用就是查找叶子节点页面。也就是说,该方法通过传入key,返回key所在的叶子节点页面。这个方法通过一个while循环实现,如果当前节点为内部节点,则调用当前节点的lookup方法得到key所对应的value**(当前节点页面可以能没有key,但因为lookup方法是upper bound算法,返回比第一个大于等于key的位置即可)**,也就得到了子节点页面的指针,如此一直循环到节点页面为叶子节点为止。返回最后的叶子节点页面即可。
fn find_leaf_page(&self, key: i32, operation: Operation, left_most: bool, right_most: bool) -> Page {
if self.root_page_.is_none() {
return None
}
let mut cur_page = self.root_page_.clone().unwrap();
while cur_page.borrow().is_internal_page() {
let child_page;
if left_most {
child_page = cur_page.borrow().value_at(0);
} else if right_most {
child_page = cur_page.borrow().value_at(cur_page.borrow().get_size() - 1);
} else {
child_page = cur_page.borrow().lookup(key);
}
assert!(child_page != ValueType::Page(None));
if let ValueType::Page(page) = child_page {
cur_page = page.unwrap();
} else {
unreachable!();
}
}
Some(cur_page)
}
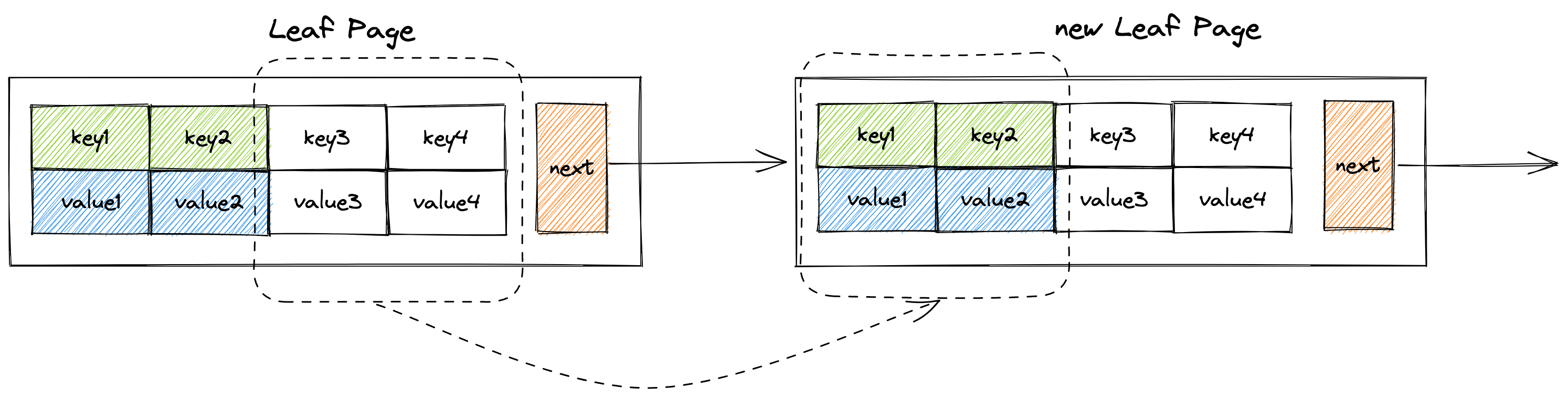
split方法
顾名思义,这个方法用于节点页面的分裂。当一个页面的size >= max size,则以为该节点页面容量已经爆了,需要分裂。而分裂的方法很简单,就是上面所提到的move_half_to方法。先new一个新的节点页面,然后将当前节点一般的键值对移动到新的节点页面中。
fn split(&mut self, cur_page: RcPage) -> Page {
if cur_page.borrow().is_internal_page() {
let new_page = BPlusTreePage::new(InternalPage, self.internal_max_size_, cur_page.borrow().get_parent_page());
cur_page.borrow_mut().move_half_to(new_page.clone());
return Some(new_page);
} else if cur_page.borrow().is_leaf_page() {
let new_page = BPlusTreePage::new(LeafPage, self.leaf_max_size_, cur_page.borrow().get_parent_page());
cur_page.borrow_mut().move_half_to(new_page.clone());
return Some(new_page);
}
None
}
insert_into_parent方法
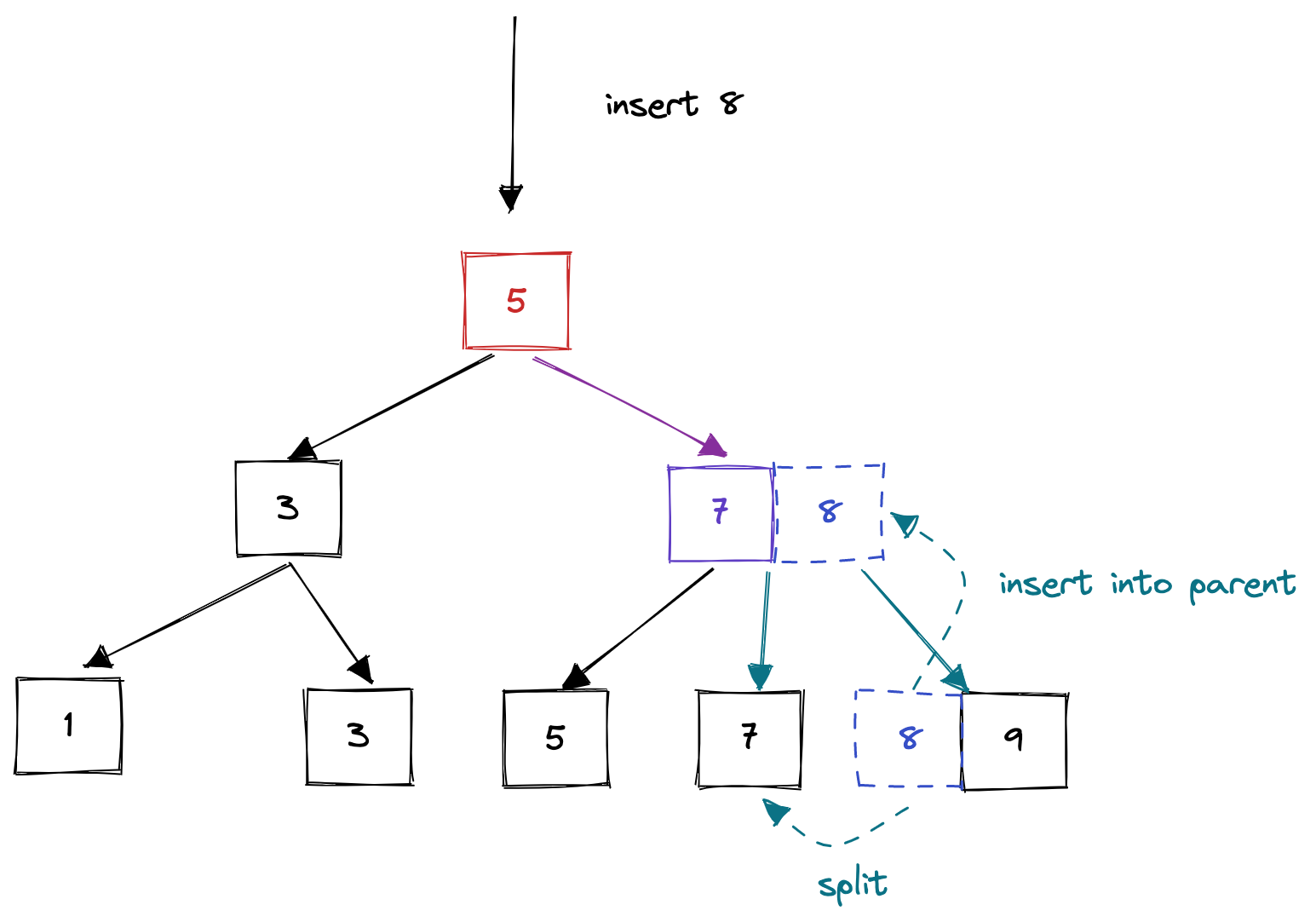
insert_into_parent方法是一个递归方法,用于递归地向parent插入新的用于索引的关键字。如图所示,当一个节点overflow后,首先执行上述的split操作,然后还需调用insert_into_parent方法,将最中间的键值对插入到父节点的相应位置。如果插入新的键值对后父节点也overflow,父节点递归的执行split方法和insert_into_parent方法,进行同样的操作,直到所有的节点都安全为止。 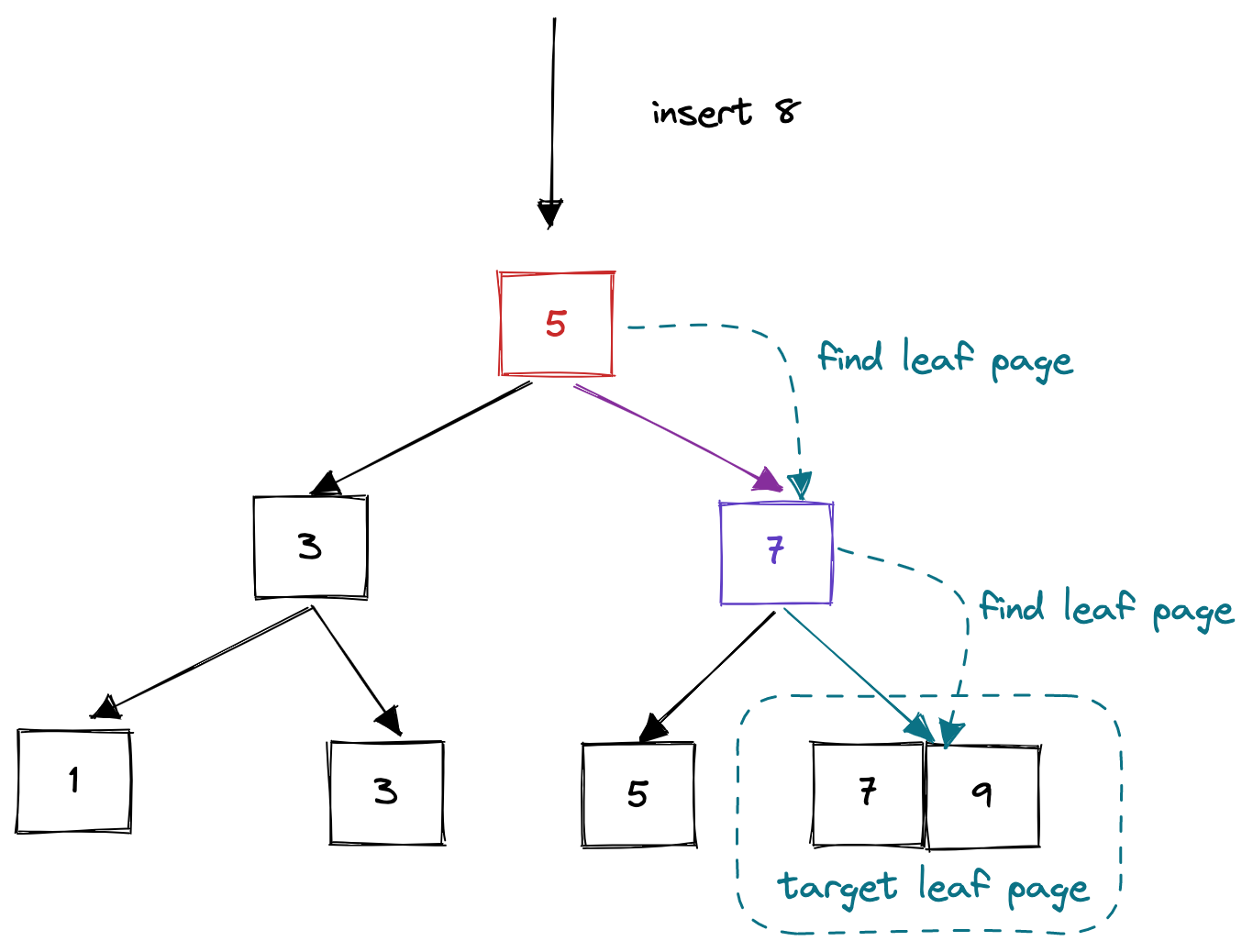
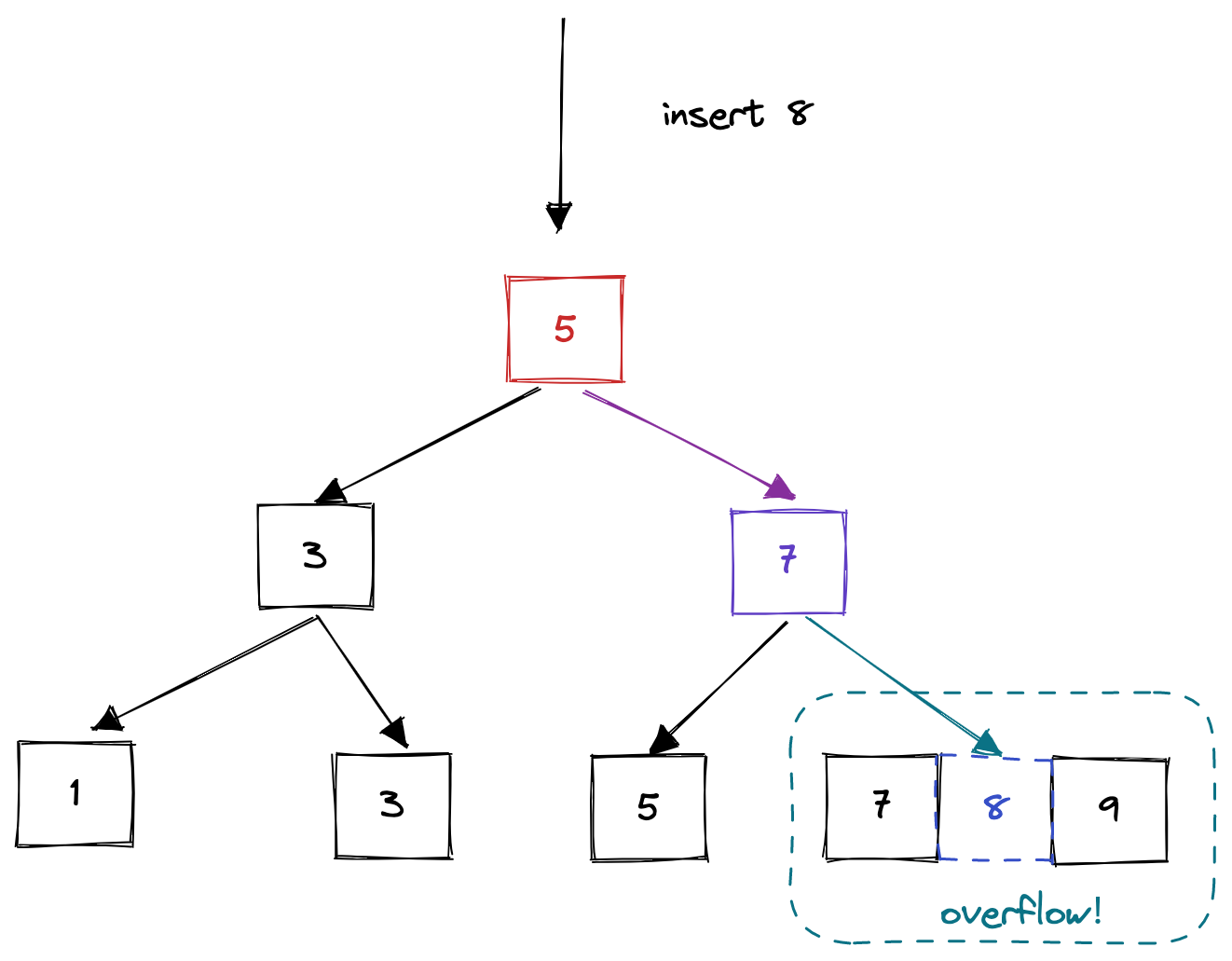
fn insert_into_parent(&mut self, old_page: RcPage, middle_key: i32, new_page: RcPage) {
if old_page.borrow().is_root_page() {
let new_root = BPlusTreePage::new(InternalPage, self.internal_max_size_, None);
new_root.borrow_mut().create_new_root(old_page.clone(), middle_key, new_page.clone());
old_page.borrow_mut().set_parent_page(Some(new_root.clone()));
new_page.borrow_mut().set_parent_page(Some(new_root.clone()));
self.root_page_ = Some(new_root);
return;
}
let parent_page = old_page.borrow().get_parent_page().unwrap();
let new_size = parent_page.borrow_mut().insert_node_after(old_page.clone(), middle_key, new_page.clone());
// TODO
new_page.borrow_mut().set_parent_page(Some(parent_page.clone()));
// -1是去掉下标为0的item
if new_size - 1 < self.internal_max_size_ {
return;
}
let new_parent_sibling_node = self.split(parent_page.clone()).unwrap();
let middle_key = new_parent_sibling_node.borrow().key_at(0);
self.insert_into_parent(parent_page.clone(), middle_key, new_parent_sibling_node.clone());
}
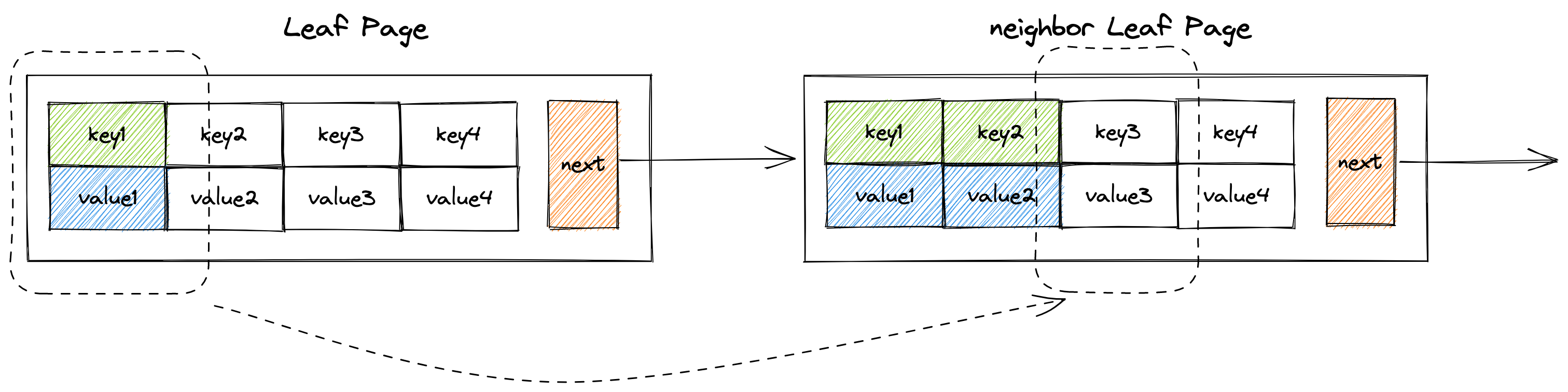
coalesce方法
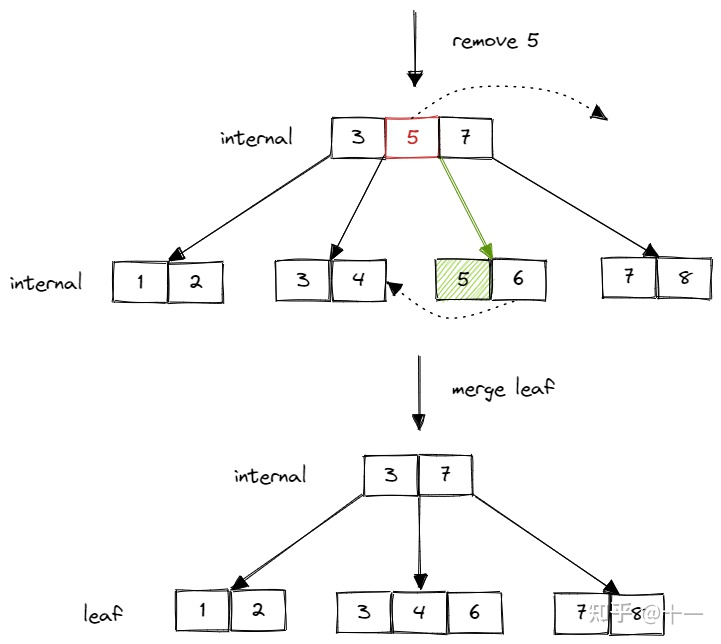
coalesce为合并的意思。也就是说,当某个节点页面的size < min size,并且与它相邻的节点也没有多余的节点借个当前节点页面,这个时候就需要执行合并操作,将当前节点页面和它的相邻页面合并成为一个节点页面,如图所示。
fn coalesce(&mut self, neighbor_page: &mut RcPage, cur_page: &mut RcPage, parent_page: RcPage, index: usize) -> bool {
let mut key_index = index;
if index == 0 {
key_index = 1;
mem::swap(cur_page, neighbor_page);
}
let middle_key = parent_page.borrow().key_at(key_index);
cur_page.borrow_mut().move_all_to((*neighbor_page).clone(), middle_key);
(*neighbor_page).borrow_mut().set_next_page(cur_page.borrow().get_next_page());
parent_page.borrow_mut().remove(key_index);
return self.coalesce_or_redistribute(parent_page.clone());
}
## B+树迭代器的实现
由于B+树的叶子节点具有next指针指向下一个叶子节点,相当于所有的叶子节点构成了一个链表。因此B+树的叶子节点天然具有迭代属性,于是可以构建一个迭代器来实现叶子节点的迭代。如下所示,`BPlusTreeIter`仅有两个属性,`cur_page_`代表当前迭代器指向的叶子节点,`index_`代表当前迭代器迭代到叶子节点的Vector 中下标为index的键值对。显然,当迭代器的`index_ == cur_page.size`时,需要将cur_page指针指向它的下一个节点,同时index更新为0。
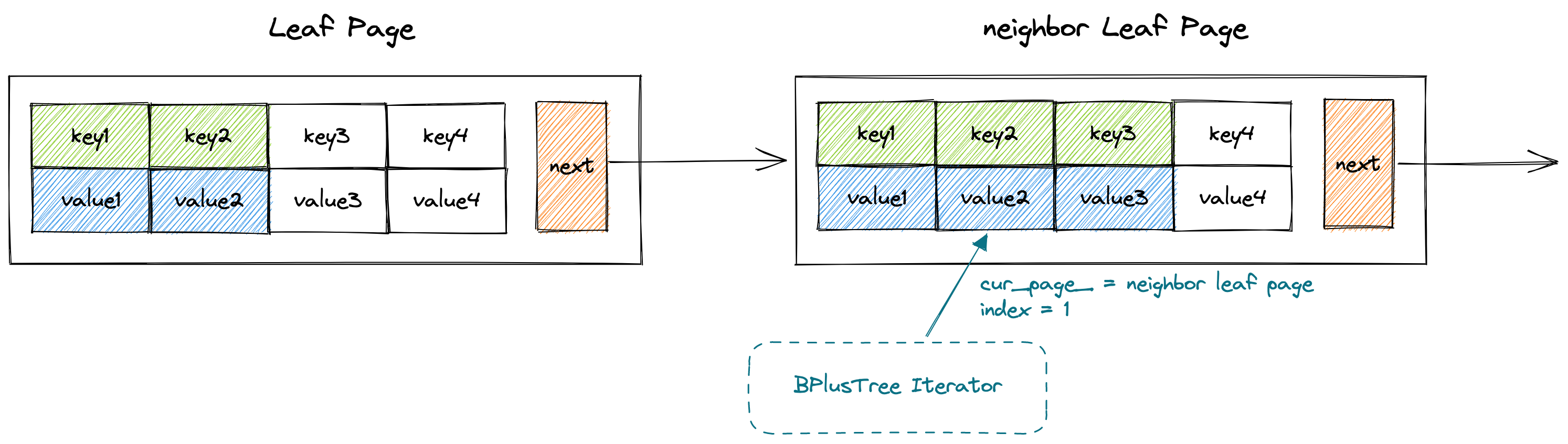
```rust
pub struct BPlusTreeIter {
cur_page_: Page,
index_: usize
}
B+树迭代器所具有的方法
impl BPlusTreeIter {
pub fn new(cur_page: Page, index: usize) -> Self {
BPlusTreeIter {
cur_page_: cur_page,
index_: index
}
}
}
impl Iterator for BPlusTreeIter {
type Item = i32;
fn next(&mut self) -> Option<Self::Item> {
if self.cur_page_.is_none() {
return None;
}
let cur_page = self.cur_page_.as_ref().unwrap();
if cur_page.borrow().get_next_page().is_none() && self.index_ == cur_page.borrow().get_size() {
return None;
}
if cur_page.borrow().get_next_page().is_some() && self.index_ == cur_page.borrow().get_size() {
let next_page = cur_page.borrow().get_next_page();
match next_page {
None => {
self.cur_page_ = None;
}
Some(next_page) => {
self.cur_page_ = Some(next_page);
}
}
self.index_ = 0;
}
return if let ValueType::Value(value) = self.cur_page_.as_ref().unwrap().borrow().value_at(self.index_) {
self.index_ += 1;
value
} else {
None
}
}
}