Sobol-Burley
A seedable Owen-scrambled Sobol sequence based on the paper Practical Hash-based Owen Scrambling by Brent Burley, but with an improved hash from Building a Better LK Hash and more dimensions due to Kuo et al.
This crate is geared towards practical graphics applications, and as such has some limitations:
- The maximum sequence length is 2^16.
- The maximum number of dimensions is 256 (although this can be worked around with seeding).
- Only
f32output is supported.
These are all trade-offs for the sake of better performance and a smaller memory footprint.
Expanding this crate to be more suitable for a wider range of applications is a tentative goal for the future. However, efficient execution for graphics applications will always be the top priority.
Basic usage
Basic usage is pretty straightforward:
use sobol_burley::sample;
// Print 1024 3-dimensional points.
for i in 0..1024 {
let x = sample(i, 0, 0);
let y = sample(i, 1, 0);
let z = sample(i, 2, 0);
println!("({}, {}, {})", x, y, z);
}
The first parameter of sample() is the index of the sample you want, and the second parameter is the index of the dimension you want. The parameters are zero-indexed, and outputs are in the interval [0, 1).
If all you want is a single Owen-scrambled Sobol sequence, then this is all you need. For more advanced usage, see the crate documentation.
Why Owen-scrambled Sobol?
There are other resources that explain this properly and in-depth, including Brent Burley's paper linked above. But here's the short version just to give some intuition:
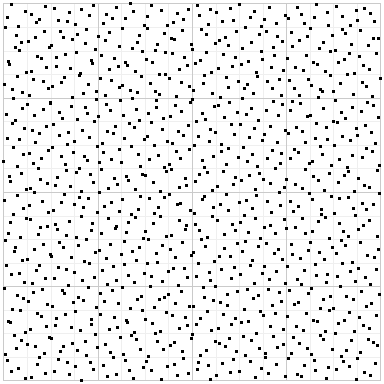
If you use random points, you get this:
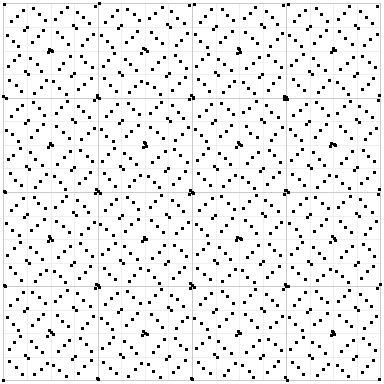
If you use plain Sobol, you get this:
But if you use Owen-scrambled Sobol, you get this:
Random points have an uneven distribution, and plain Sobol exhibits a strong structure that can result in bias and artifacts. But Owen-scrambled Sobol in some sense gets the best of both worlds: the even distribution of Sobol, but randomized to minimize structure.
Unsafe code
This crate uses unsafe code for SIMD acceleration. For 100% safe code, you can disable SIMD support via the simd feature flag (enabled by default).
License
The main code in this project is licensed under either of
- MIT license (licenses/MIT.txt or http://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
- Apache License, Version 2.0, (licenses/APACHE-2.0.txt or http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0)
at your option.
The Sobol direction numbers under direction_numbers/ and some of the code in build.rs (demarcated by comments) is adapted from work by Stephen Joe and Frances Y. Kuo, and is under the 3-clause BSD license. See licenses/JOE_KUO.txt for details.
Contributing
Contributions are absolutely welcome! Please keep in mind that this crate aims to be:
- no-std and allocation-free. PRs that use allocation, etc. are very likely to be rejected.
- As small as it reasonably can be, including transitive dependencies. PRs that pull in dependencies--especially deep dependency trees--are likely to be rejected unless they really pull their weight.
Unless you explicitly state otherwise, any contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in this project by you will be licensed as above (MIT/Apache dual-license), without any additional terms or conditions.